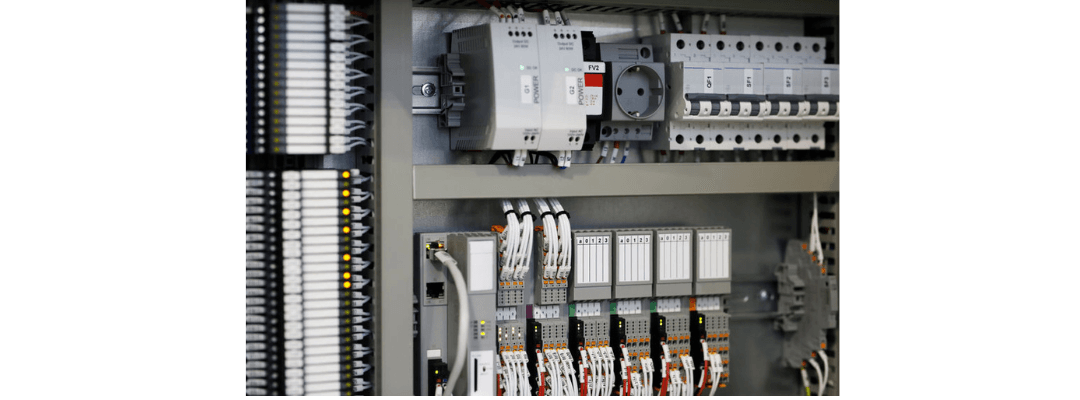
Automation control panels must adhere to specific standards and ratings to ensure their safety, reliability, and performance across different industries and applications. These standards govern aspects like electrical design, construction, safety features, and environmental protection. Below are the key standards, ratings, and certifications relevant to automation control panels:
Key Automation Control Panel Standards
Below are the most widely adopted standards for automation control panels:
1. IEC 61439 (International Standard)
- Governs low-voltage switchgear and control gear assemblies
- Focuses on design verification, performance, and safety
- Ideal for global applications and projects requiring international compliance
2. UL 508A (United States)
- U.S. standard for industrial control panels
- Specifies component selection, wire sizing, protection methods, and labeling
- Panels built to UL 508A are listed for safety by Underwriters Laboratories
3. NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code – NEC)
- Ensures safe electrical installation practices in the U.S.
- Covers conductor sizing, overcurrent protection, grounding, and circuit design
- Highly relevant for hazardous location control panels
4. CSA C22.2 No. 14 (Canada)
- Canadian standard for electrical equipment in industrial applications
- Similar to UL 508A with some variations in component and enclosure guidelines
5. CE Marking (European Union)
- Mandatory for exporting electrical equipment to the EU
- Requires compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD), EMC Directive, and Machinery Directive
Important Ratings for Control Panels
Understanding panel ratings is critical for selection and installation. Key parameters include:
1. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
- Indicates resistance to dust and water
- Example: IP65 – Dust tight and protected against water jets
- Choose higher IP ratings for outdoor or washdown environments
2. NEMA Rating (North America)
- Defines enclosure protection against dust, water, oil, and corrosion
- Example: NEMA 12 – Ideal for indoor industrial applications
3. Short Circuit Current Rating (SCCR)
- Measures the maximum current the panel can safely withstand during a short circuit
- Essential for ensuring system and worker safety in fault conditions
4. Voltage & Ampere Rating
- Panels should be clearly labeled with their operating voltage and current handling capacity
- Proper sizing prevents overheating, failure, and inefficiency
5. Temperature and Environmental Ratings
- Ensures that panels perform reliably in high or low ambient temperatures
- May require cooling or heating solutions depending on the environment
AutomationDirect’s Commitment to Quality and Compliance
At AutomationDirect, we manufacture and deliver automation control panels that meet:
- IEC, UL, NFPA, and CE requirements
- Industry-specific demands like HVAC, water treatment, material handling, and process automation
- Custom-built configurations with certified components
We also provide thorough documentation, testing, and panel drawings to ensure easy installation and regulatory inspections.

Recent Comments