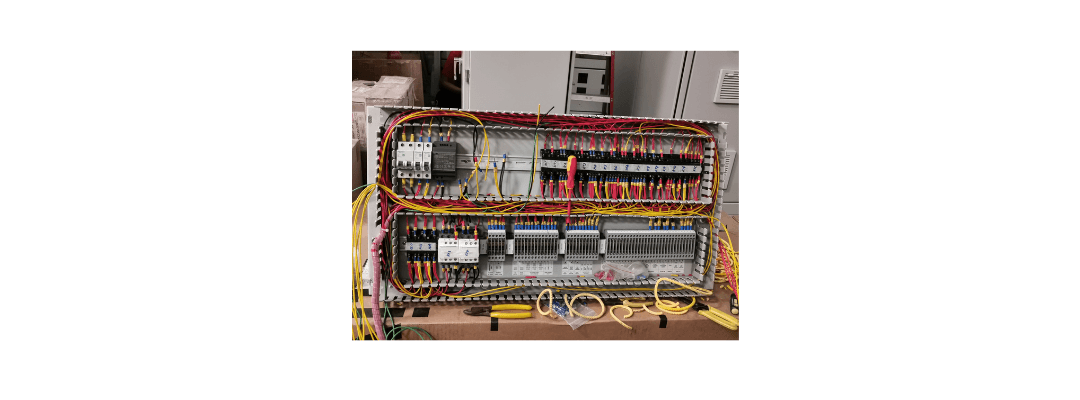
Key Components of an Automation Control Panel and Their Functions
Automation control panels are made up of several essential components, each playing a crucial role in the operation and control of industrial processes. Here are the key components and their functions:
1. Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
- Function: The brain of the control panel, a PLC is responsible for executing automated tasks based on input signals from sensors and devices. It processes these inputs according to its programming and sends commands to actuators, motors, or other outputs.
- Purpose: To provide control logic for processes like machine operation, production lines, and systems monitoring.
2. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
- Function: An HMI provides a visual interface between the operator and the machine. It displays system status, process data, and allows for manual control and adjustments.
- Purpose: To enable easy control and monitoring of the system, allowing operators to interact with the machine in real time.
3. Power Supply
- Function: This component converts incoming electrical power (AC or DC) into the necessary voltage and current levels required by various devices within the control panel.
- Purpose: To provide consistent and reliable power to the control devices, ensuring smooth operation.
4. Relays and Contactors
- Function: Relays and contactors are used to control high-power electrical circuits with a low-power signal from the PLC or another control device.
- Purpose: To safely and efficiently switch electrical loads on or off, controlling motors, lighting, and other equipment.
5. Circuit Breakers and Fuses
- Function: Fuses and Circuit Breakers components provide overcurrent protection, automatically disconnecting circuits in the event of an overload or short circuit.
- Purpose: To protect the control panel and connected devices from damage due to electrical faults.
6. Input/Output (I/O) Modules
- Function: I/O modules connect sensors, switches, and other input devices to the PLC, and connect the PLC to output devices like motors, solenoids, and indicators.
- Purpose: To facilitate communication between the physical devices in the system and the PLC, enabling data collection and execution of control commands.
7. Terminal Blocks
- Function: Terminal blocks provide a point of connection for wiring, making it easier to organize, secure, and distribute power and signals to various components.
- Purpose: To ensure neat and accessible wiring, simplifying troubleshooting and maintenance.
8. Wires and Cables
- Function: Wires and cables transmit power and signals between components within the control panel and to external devices.
- Purpose: To provide reliable electrical connections between all components, ensuring proper communication and power distribution.
9. Switches and Push Buttons
- Function: These manual control devices allow operators to start, stop, or reset the system manually.
- Purpose: To give users direct control over certain aspects of the automation system for operational flexibility.
10. Enclosure
- Function: The enclosure houses and protects all the internal components of the control panel from external environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and temperature variations.
- Purpose: To ensure the safety and longevity of the control system while complying with industry standards for protection and accessibility.
11. Communication Modules
- Function: These modules facilitate data exchange between the control panel and other systems or networks, often using industrial communication protocols like Ethernet, Modbus, or Profibus.
- Purpose: To enable remote monitoring, data logging, and integration with broader automation or enterprise systems.
12. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
- Function: VFDs control the speed and torque of AC motors by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor.
- Purpose: To optimize energy consumption, enhance motor performance, and provide precise control over industrial processes.
13. Safety Components
- Function: Safety relays, emergency stop buttons, and light curtains are designed to ensure the safe operation of the control panel, shutting down the system in the event of hazardous conditions.
- Purpose: To protect both personnel and equipment by mitigating risks associated with machine operation.
14. Timers and Counters
- Function: Timers delay the execution of certain actions, while counters track the number of events, such as production cycles.
- Purpose: To allow for time-based operations and tracking within the control system, enhancing precision and efficiency.
These components work together to form a cohesive automation control system, ensuring efficient, reliable, and safe operations in industrial settings.

Recent Comments